Planning the Anzo and EKS Network Architecture
This topic describes the network architecture that supports the Anzo and EKS integration.
When you deploy the K8s infrastructure, Cambridge Semantics strongly recommends that you create the EKS cluster in the same VPC as Anzo. If you create the cluster in a new VPC, you must configure the new VPC to be routable from the Anzo VPC.
The diagram below shows the ideal network architecture to employ when the EKS cluster infrastructure is integrated with Anzo. Several of the network resources shown in the diagram are automatically deployed (and the appropriate routing is configured) according to the values that you supply in the cluster and node group .conf files in the eksctl package (see Cluster Creation Scripts and Configuration Files).
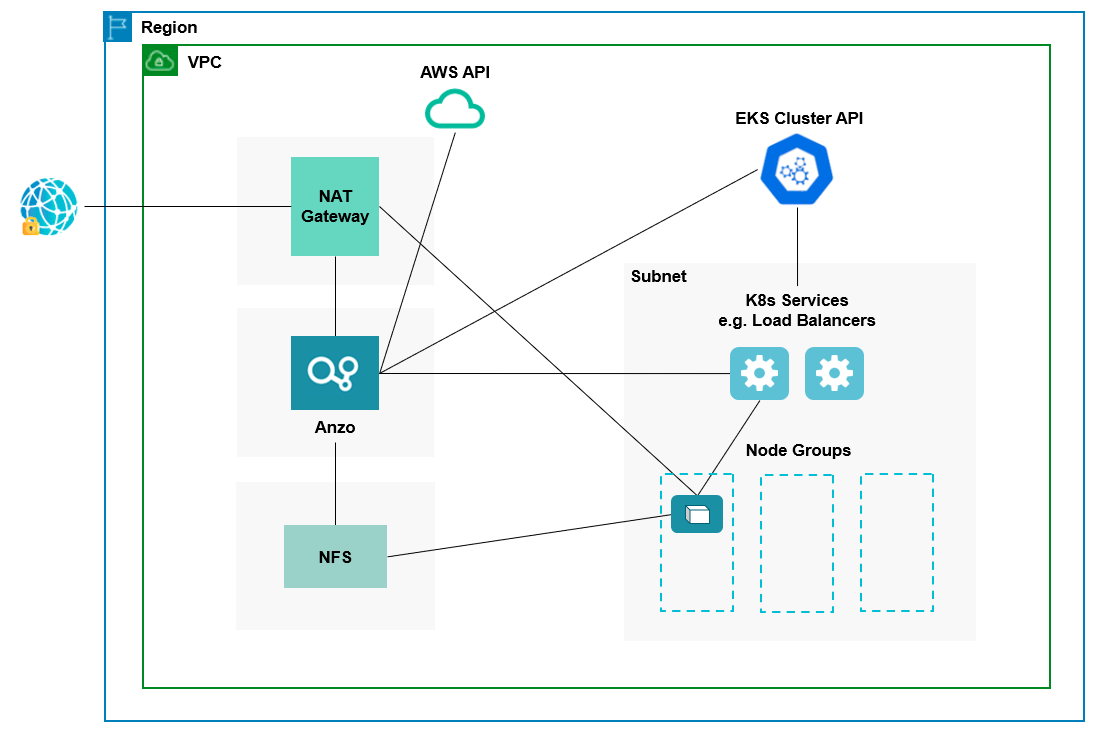
In the diagram, there are two components that you deploy before configuring and creating the K8s resources:
- Anzo: Since the Anzo server is typically deployed before the K8s components, you specify the Anzo VPC ID when creating the EKS cluster, ensuring that Anzo and all of the EKS cluster components are in the same network and can talk to each other. Also, make sure that Anzo has access to the AWS and EKS APIs.
- NFS: You are required to create a network file system (NFS). However, Anzo automatically mounts the NFS to the nodes when AnzoGraph, Anzo Unstructured, Spark, and Elasticsearch pods are deployed so that all of the applications can share files. See Deploying the Shared File System for more information. The NFS does not need to have its own subnet but it can.
The rest of the components in the diagram are automatically provisioned when the EKS cluster and node groups are created. The eksctl scripts create NAT gateways and subnets for outbound internet access, such as for pulling container images from the Cambridge Semantics repository. In addition, the scripts create a subnet for the K8s services and node groups and configure the routing so that Anzo can communicate with the K8s services and the services can talk to the pods that are deployed in the node groups.
For alternative network architecture that does not include a NAT gateway and is locked down to all public traffic, contact Cambridge Semantics about setting up a service engagement.
To get started on creating the EKS infrastructure, see Creating and Assigning IAM Policies for instructions on creating the IAM policies that are needed for assigning permissions to create and use the EKS cluster.