Creating a Cloud Filter
Cloud filters display values in term clouds where each term is written in a font size that represents the number of results for that value. Unlike list filters, which enable you to select and filter on multiple values at once, cloud filters allow you to filter on one value at a time. The Cloud filter is available for all data types.
Follow the instructions below to create a Cloud Filter.
- Open the Dashboard that you want to add the filter to.
- In the Hi-Res Analytics main toolbar, click Filters and select Create a Filter. The Create Filter dialog box is displayed.
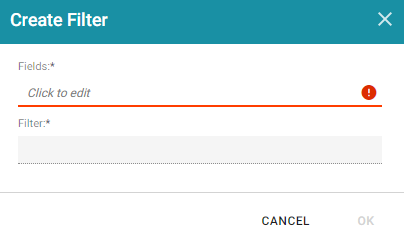
- Click in the Fields field to open the Property drop-down list and determine the property to filter on. The values for this property will be the terms that are displayed in the cloud. The list of available properties depends on the selected Data Type for the Dashboard.
For example, the following image shows the list of properties that are available for a Dashboard whose source is a Graphmart that contains data about tickets sold for various types of events. The Data Type for the Dashboard is tickit_events:
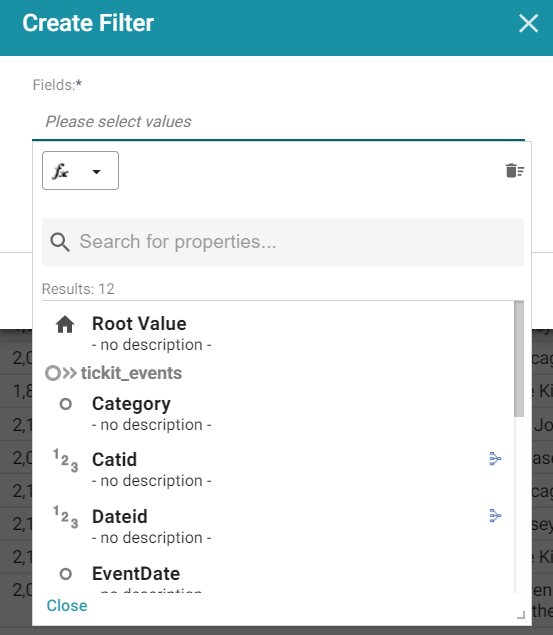
The list below describes the icons and options that are available when choosing a property:
- The Root Value (
 ) is the instance URI for the root resource—the URI for the instances of the class that was chosen as the Data Type for the Dashboard.
) is the instance URI for the root resource—the URI for the instances of the class that was chosen as the Data Type for the Dashboard. To view the Root Value values, you can use the STR function to show a string representation of the URIs.
- Linked classes are represented by incoming (
 ) and outgoing (
) and outgoing ( ) connection icons. The properties in those classes with a path to another class are denoted with a circle icon (
) connection icons. The properties in those classes with a path to another class are denoted with a circle icon ( ). Selecting a linked property navigates to that class and displays its properties.
). Selecting a linked property navigates to that class and displays its properties. - When a property or path is selected, the breadcrumbs at the top of the dialog box show you the property path. You can click the Clear icon (
 ) to clear the path and start again.
) to clear the path and start again. - After you have selected a property, you can apply a function or formula to that property to calculate the values that are displayed in the filter. To add a function, click the function button (fx) at the top of the drop-down list. The functions that become available depend on the data type of the selected property. To choose a more advanced function or type a formula, click Advanced. The Calculated Value dialog box opens and enables you to choose additional properties and functions. For more information, see Calculating Values in Lenses and Filters.
- The Root Value (
- After you have selected the property to filter on, click Close to close the Fields drop-down list.
- Next, click the Filter field and select Cloud from the drop-down list. The dialog box is refreshed to show the Filter Properties and other options that are available for the filter type:
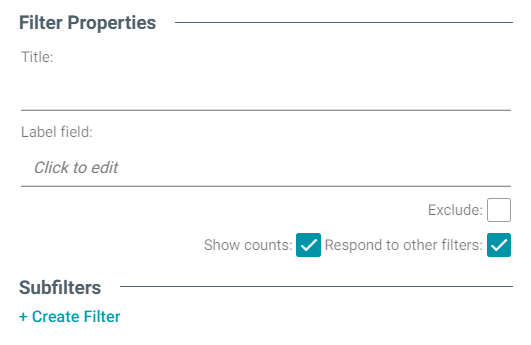
- Configure any of the following properties. All of the fields are optional:
- Title: Defines the title that appears at the top of the filter when it is added to the Dashboard. If Title is blank, the value from the Fields field is used as the title.
- Label Field: If you want to populate the cloud with values from a property other than the one specified in Fields, you can select an alternate property in this field.
- Exclude: This setting controls whether selecting a term in the Cloud Filter narrows the results to show only the records that include that term or whether selecting a term excludes the records that include that term. When Exclude is disabled, selecting a term narrows the Dashboard results to show only the records that include that term. When Exclude is enabled, selecting a term filters out all of the records that include that term.
- Show Counts: This setting controls whether the number of results for each term are displayed when you hover the pointer over a term.
- Respond to Other Filters: This setting controls whether the results of this filter change based on selections in other filters on the Dashboard.
- If you would like to be able to further constrain the data that appears in the filter, you can add one or more subfilters. To add a subfilter, click Create Filter under Subfilters. The process of creating a subfilter is the same as the process for the parent filter. However, the subfilter is not displayed on the Dashboard. It is visible only when editing the parent filter, and the subfilter's configuration affects only the parent filter and any sibling subfilters.
- When you have finished configuring the filter, click OK to add it to the Dashboard. The new filter appears in the left pane of the Dashboard and displays the values that are available for filtering the displayed data.
For example, the filter in the image below shows cities with event venues. The size of the terms represent the number of events that were held in venues in that city.
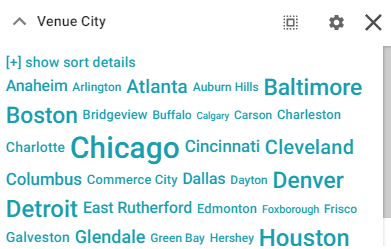
Depending on whether the Exclude option is enabled or disabled, clicking a term in the Cloud refreshes the Dashboard to show only the data that either contains or excludes the selected term.
When working with the filter on the Dashboard, the following options are available for sorting and configuration:
- show/hide sort details: Shows or hides the following options for sorting the results in the filter:
- Sort by: Select Value to sort string values alphabetically, or select Count to order results according to the total number of results for each value.
- Direction: Select Ascending to order results in alphabetical order. Or select Descending to order results in reverse order.
- show/hide filters: This option is displayed when a term is selected in the Cloud. It shows or hides the selection.
- Select All Visible (
 ): This option does not work for Cloud Filters.
): This option does not work for Cloud Filters. - Clear (
 ): This option becomes available when a term is selected. Clicking Clear removes the selection.
): This option becomes available when a term is selected. Clicking Clear removes the selection. - Designer (
 ): Clicking this icon opens the filter Designer so that you can view or change the filter configuration.
): Clicking this icon opens the filter Designer so that you can view or change the filter configuration. - Close (X): Clicking Close removes the filter from the Dashboard. This action cannot be undone.