Anzo K8s Requirements
This section gives an overview of the general infrastructure requirements for Anzo K8s integration. Additional software, network infrastructure, and permission-related requirements are included in the deployment instructions for each of the cloud service providers.
- Supported Kubernetes Versions
- File Storage Requirements
- Node Pool Requirements
- Container Registry Requirements
Supported Kubernetes Versions
The table below shows the supported Kubernetes (K8s) versions by Cloud Service Provider (CSP):
| CSP | K8s v1.17 | K8s v1.18 | K8s v1.19 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon EKS |

|

|

|
| Google GKE |

|

|

|
| Azure AKS |

|

|
File Storage Requirements
A network file system (NFS) is required for shared file storage between Anzo and the dynamic applications. You are required to create the file system. However, Anzo automatically mounts the NFS to the nodes when AnzoGraph, Anzo Unstructured, Spark, or Elasticsearch pods are deployed. See Deploying the Shared File System for more information.
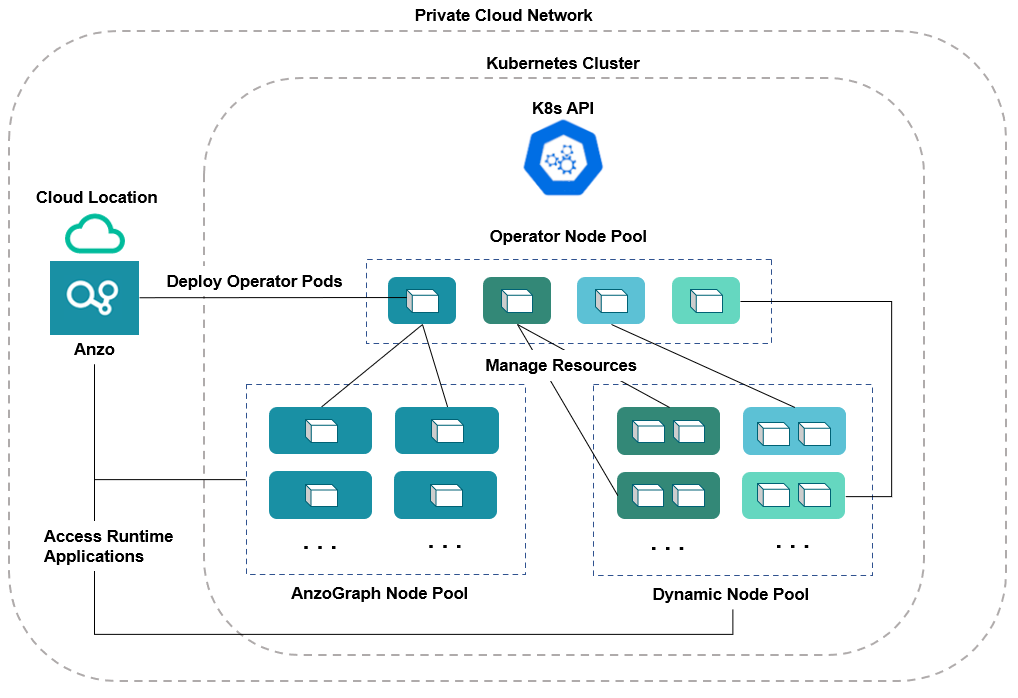
Node Pool Requirements
There are three types of node pools or node groups that you are required to configure for integration with Anzo. In addition to the scripts for creating and configuring the K8s cluster, Cambridge Semantics supplies configuration files to use as templates for defining the policies for each type of node pool. The node pools can be configured as static or autoscaling.
Operator Node Pool
An Operator node pool is tuned to run operator pods. Operator pods manage the application pods and control the K8s resources of the applications that are deployed in the node pools. There is one operator for each application: AnzoGraph, Elasticsearch, Anzo Agent and Anzo Unstructured, and Spark. Anzo deploys and manages the operator pods. With the help of the operators, Anzo orchestrates the provisioning and deprovisioning of the application nodes and pods. Since the operators in the Operator node pool are required to be active at all times, operator pods are designed to be very small and use very few resources. They can be deployed on standard, small-sized cloud instances.
AnzoGraph Node Pool
An AnzoGraph node pool is tuned to run AnzoGraph pods. AnzoGraph node pools are typically configured to auto-scale so that nodes are not deployed unless a user requests an AnzoGraph environment for loading a graphmart or running queries against the data in a graphmart.
Dynamic Node Pool
The Dynamic node pool is tuned to run Elasticsearch, Spark, Anzo Agent, and Anzo Unstructured (AU) pods. Dynamic node pools are also typically configured to auto-scale so that nodes are not deployed unless a user requests an environment for running a structured or unstructured pipeline.
The diagram below shows the K8s cluster architecture with the required node pools.
For Amazon EKS deployments, there is a fourth type of required node group. The additional type, called a Common node group, is tuned to run K8s service pods, such as Cluster Autoscalers and Load Balancers.
For guidance on choosing the instance types and sizes for the nodes in the required node pools, see Compute Resource Planning.
Container Registry Requirements
You are not required to set up an internal container registry for Anzo and K8s integration. However, if your K8s cluster will not have outbound internet access for retrieving container images from the Cambridge Semantics repository, you will need to create a container registry through your Cloud Service Provider.