Server and Cluster Requirements
The following sections detail the minimum requirements and recommendations to follow for setting up AnzoGraph host servers and cluster environments.
Hardware Requirements
Cambridge Semantics lists above average production system hardware requirements as a guideline. Large production data sets running interactive queries may require significantly more powerful hardware and RAM configurations. Provision production server hardware accordingly to avoid performance issues.
| Component | Minimum | Recommended | Guidelines | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Available RAM | 16 GB (for small-scale testing only) | 200 GB or more | AnzoGraph needs enough RAM to store data, intermediate query results, and run the server processes. Cambridge Semantics recommends that you allocate 3 to 4 times as much RAM as the planned data size. Do not overcommit RAM on a VM or on the hypervisor/container host. Avoid memory paging to disk (swapping) to achieve the highest possible level of performance. For more information about determining the server and cluster size that is ideal for hosting AnzoGraph, see Server and Cluster Sizing and Capacity Planning Guidelines. | ||
| Disk space and type | 10 GB HDD |
200+ GB SSD |
AnzoGraph requires 10 GB for internal requirements. The amount of additional disk space required for load file staging, persistence, or backups depends on the size of the data to be loaded. For persistence, Cambridge Semantics recommends that you have twice as much disk space on the local AnzoGraph file system as RAM on the server. | ||
| CPU (Intel only) | 2 cores | 32 cores | Once you provision sufficient RAM and a high-performing I/O subsystem, performance depends on raw CPU capabilities. Always use multi-core CPUs. A greater number of cores can make a dramatic difference in the performance of interactive queries. AnzoGraph does not support AMD processors at this time. | ||
| Networking | 10gbE | 20+gbE |
Not applicable for single server installations. Since AnzoGraph is high performance computing (HPC) Massively Parallel Processing (MPP) OLAP engine, inter-cluster communications bandwidth dramatically affects performance. AnzoGraph clusters require optimal network bandwidth.
In a switched network, make sure that all NICs link to the same Top Of Rack or Full-Crossbar Modular switch. If possible, enable SR-IOV and other HW acceleration methods and dedicated layer 2 networking that guarantees bandwidth. |
Clusters and Virtual Environments
AnzoGraph requires that all elements of the infrastructure provide the same quality of service (QoS). Do not run AnzoGraph on the same server as any other software except when in single-server mode and with an expectation of lowered performance. Providing the same QoS is especially important when using AnzoGraph in a clustered configuration. If any of the servers in the cluster perform additional processing, the cluster becomes unbalanced and may perform poorly. A single poor performing server degrades the other servers to the same performance level. All nodes require the same hardware specification and configuration. Also use static IP addresses or make sure that DHCP leases are persistent.
To ensure the maximum and most reliable QoS for CPU, memory, and network bandwidth, do not co-locate other virtual machines or containers (such as Docker containers) on the same hypervisor or container host. For hypervisor-managed VMs, configure the hypervisor to reserve the available memory for the AnzoGraph server. For clusters, make sure there is enough physical RAM to support all of the AnzoGraph servers, and reserve the memory via the hypervisor.
In addition, running memory compacting services such as Kernel Same-page Merging (KSM) impacts CPU QoS significantly and does not benefit AnzoGraph. Live migrations also impact the performance of VMs while they get migrated. While live migration can provide value for planned host maintenance, AnzoGraph performance may be impacted if live migrations occur frequently. For more information about Kernel Same-page Merging, see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kernel_same-page_merging.
| Note | Advanced configurations may benefit from CPU pinning on the hypervisor host and disabling CPU hyper-threading. For more information about CPU pinning, see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Processor_affinity. For information about hyper-threading, see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyper-threading. |
Cambridge Semantics can provide benchmarks to establish relative cluster performance metrics and validate the environment.
Software Requirements
The table below lists the software requirements for AnzoGraph servers.
| Component | Requirement | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operating System | RHEL 7.4+, CentOS 7.4+ | See Tuning User Resource Limitations (ulimits) below for information about setting ulimits.
|
||
| GNU Compiler Collection | Installed | Install the latest version of the GCC tools for your operating system. See Installing GCC below. |
Installing GCC
Run the following command to install GCC:
sudo yum install gcc
Specifically, AnzoGraph requires the glibc, glibc-devel, and gcc-c++ libraries. Typically, when you install GCC by running yum install gcc, those libraries are included as part of the package. In rare cases, depending on the host server configuration, installing GCC excludes certain libraries. If AnzoGraph fails to start and you receive a "Compilation failed" message, it may indicate that some of the required libraries are missing. To install the missing libraries, run the following command:
sudo yum install glibc glibc-devel gcc-c++
Tuning User Resource Limitations (ulimits)
Cambridge Semantics recommends that you tune the user resource limits (ulimits) for your Linux distribution to increase the limits for the following resources:
- Increase the open files limit to at least 4096.
- Increase the limit for the following resources to unlimited:
- cpu time
- file locks
- file size
- max memory size
- max user processes
- virtual memory
To view the current ulimits, run ulimit -a. To permanently change ulimits, modify the /etc/security/limits.conf file. For more information, see How to set ulimit values in the RHEL support documentation.
| Note | Also make sure that the Linux environment variables http_proxy and https_proxy are not set. The Anzo gRPC protocol cannot make connections to the database when proxies are enabled. |
Optional Software
| Program | Description |
|---|---|
| vim | Editor for creating or changing files. |
| sudo | Enables users to run programs with alternate security privileges. |
| net-tools | Networking utilities. |
| psutils | Python system and process utilities for retrieving information on running processes and system usage. |
| tuned | Linux system service to apply tunables. |
| wget | Utility for downloading files over a network. |
| Google SDK | For virtual servers on Google Cloud Engine (GCE). Command line tool to enable syncing of data from Google storage. You can download the latest version from Google: https://cloud.google.com/sdk/. |
Firewall Requirements
AnzoGraph servers communicate via TCP/IP sockets. Client applications connect to AnzoGraph using the standard SPARQL HTTP(S) protocol. Cambridge Semantics applications, such as the AnzoGraph front end, communicate with the database via the secure, encrypted, gRPC-based protocol.
| Important | For AnzoGraph clusters, all servers in the cluster must be in the same network. Make sure that all instances are in the same VLAN, security group, or placement group. |
Open the TCP ports listed in the table below. This image shows a visual representation of the communication ports:
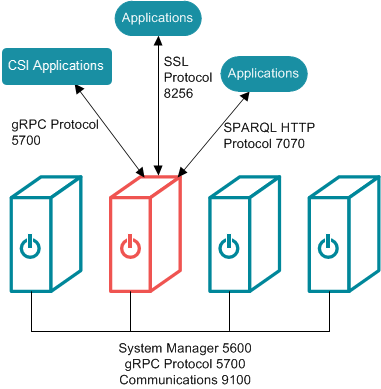
| Port | Description | Access needed... |
|---|---|---|
| 5700 | gRPC protocol port for secure communication between AnzoGraph servers. |
|
| 8256 | SPARQL HTTPS port for SSL communication between applications and AnzoGraph. |
|
| 7070 | SPARQL HTTP port for communication between applications and AnzoGraph. |
|
| 9100 | The internal fabric communications port. |
|
| 5600 | The SSL system management port. |
|