Supported Mapping Functions
This topic describes the mapping functions that Anzo supports. For information about adding functions to mappings, see Transforming Data in Mappings.
- Aggregate Functions
- Boolean Operators
- Conditional Expressions
- Data Type Conversion Functions
- Lookup and Mapping Functions
- Numeric Functions
- String Functions
Aggregate Functions
Aggregate functions rely on the groups that you define by configuring a GROUP BY statement for the mapping. All aggregate functions use the GROUP BY that you specify. Follow these instructions to configure a GROUP BY statement:
- Click the cell to the left of the target table name to open the menu. For example:
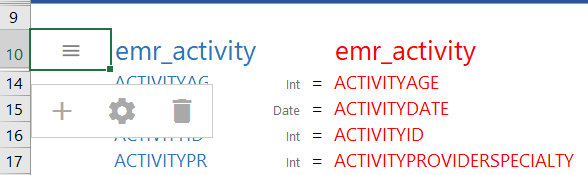
- Click the Cog icon (
 ) in the menu to open the configuration section of the mapping.
) in the menu to open the configuration section of the mapping.
- In the configuration section, click the cell that contains the join, filter, group by... text in the Target column. If necessary, click the drop-down arrow next to the cell to open the Configure text box.
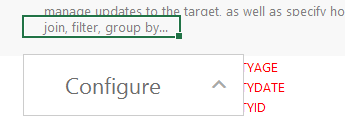
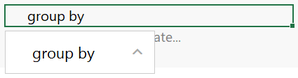
- In the Configure text box, start typing "group by." Anzo completes the text and displays group by in the box. Click the up arrow to enter group by in the cell.
- Click the cell in the Source column that corresponds to the group by you entered in the Target column. Anzo enters GROUP BY in the Source text box.
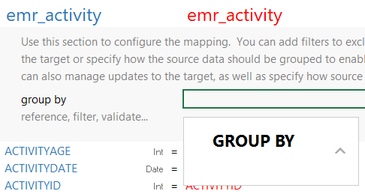
- In the Source text box, click under GROUP BY and start typing column names for the columns that you want to group on. Press Ctrl + to enter multiple columns. Then click the up arrow to enter the columns in the cell. For example:

When you finish configuring the GROUP BY, save the mapping. When you use aggregate functions in the mapping, the functions group data according to the configured GROUP BY.
The table below describes the supported aggregate functions.
| Function & Arguments | Description |
|---|---|
| AVG number |
This function calculates the arithmetic mean for the group of numeric values that you specify in the number argument.
For example, the following source mapping calculates the average NUMBER_OF_BYTES for each event. The GROUP BY statement for the mapping includes EVENTID.  |
| COUNT value |
This function counts the number of instances for a grouped value. This function does not perform COUNT DISTINCT. |
| MAX value |
This function calculates the maximum value for the group of numeric values that you specify in the value argument. |
| MIN value |
This function calculates the minimum value for the group of numeric values that you specify in the value argument. |
| SUM number |
This function calculates the sum of the group of numeric values that you specify in the number argument. |
Boolean Operators
This section describes the boolean operators that you can use to target specific data and expand or reduce the number of records that are returned.
| Function & Arguments | Description |
|---|---|
| EQUAL value1 |
This function compares numeric values and returns "true" if value1 is equal to value2 and "false" if the values are not equal (value1 = value2).
|
| GE value1 |
This function compares numeric values and returns "true" if value1 is greater than or equal to value2 and "false" if value1 is less than value2 (value1 >= value2).
|
| GT value1 |
This function compares numeric values and returns "true" if value1 is greater than value2 and "false" if value1 is less than or equal to value2 (value1 > value2).
|
| IN value |
This function checks whether a given value exists in a set of values (set to check). If the value exists in the set, IN returns "true." If the value does not exist in the set, IN returns "false." IN does not do comparisons on string values.
For example, the following source mapping checks to see if PATIENTID falls in the set of 1, 100, 1000:
|
| ISNULL expression |
This function evaluates the source column values in expression and returns "true" if the value is null and "false" if it is not null. You must choose a column in the expression argument; do not type a literal value or a function. |
| LE value1 |
This function compares numeric values and returns "true" if value1 is less than or equal to value2 and "false" if value1 is greater than value2 (value1 <= value2).
|
| LT value1 |
This function compares numeric values and returns "true" if value1 is less than value2 and "false" if value1 is greater than or equal to value2 (value1 < value2).
|
| NOT_EQUAL value1 |
This function compares numeric values and returns "true" if value1 does not equal value2 and "false" if the values are equal (value1 != value2).
|
Conditional Expressions
This section describes the functions that you can use to perform different computations based on whether a conditional expression evaluates to true or false.
| Function & Arguments | Description |
|---|---|
| AND logical1 |
This logical function evaluates two or more logical statements (logical1, logical2) and returns "true" if all conditions are met or "false" if any condition is not met. All logical statements must evaluate to the same data type.
|
| IF test
|
This function evaluates the condition in the test argument and assigns the value in value if true or value if false based on the results.
|
| OR logical1 |
This logical function evaluates two or more logical statements (logical1, logical2) and returns "true" if any of the conditions are met or "false" if none of the conditions are met. All logical statements must evaluate to the same data type.
|
| NOT logical |
This logical function evaluates whether data does not meet the condition (logical) that you specify.
|
| REPLACEIFNULL expression
|
This function evaluates the expression. If the result is null, Anzo replaces the null with the value in if null expression.
For example, the source mapping below replaces any null values in the PATIENTID integer column with the integer 999:
|
| REPLACEIFNULLOREMPTY string expression
|
This function evaluates the string expression. If the result is null or empty (""), Anzo replaces the empty or null with the value in if null or empty expression.
For example, the source mapping below replaces any null or empty values in the GENDER column with "Not Specified":
|
Data Type Conversion Functions
This section describes functions that you can use to convert values from one data type to another.
| Function & Arguments | Description |
|---|---|
| BOOLEANPARSE value |
This function converts a string (value) that contains "true" and "false" values to boolean format. Specifying a source column for which some instances do not contain "true" or "false" values can cause the ETL job to fail. Cambridge Semantics recommends using TRYPARSEBOOLEAN unless you are certain that all instances of value contain the words "true" or "false." |
| DATEPARSE date text
|
This function converts a string that contains a date value (date text) to the specified date format. Specifying a source column for which some instances do not contain date values can cause the ETL job to fail. Cambridge Semantics recommends using TRYPARSEDATE unless you are certain that all instances of date text contain a date.
For example, the source mapping below converts the MovieReleaseDate values from strings to dates in the format "dd-MM-yyyy":
The format that you specify for dates is flexible. For example, typing the format "dd-MMM-yy" displays values such as "01-JAN-19." |
| DATETIMEPARSE date text
|
This function converts a string that contains a datetime value (date text) to the specified date format. Specifying a source column for which some instances do not contain datetime values can cause the ETL job to fail. Cambridge Semantics recommends using TRYPARSEDATETIME unless you are certain that all instances of date text contain a datetime.
For example, the source mapping below converts the PATIENTLASTPMODATE from a string value to a datatime value in the format "MM-dd-yyyy HH:mm:ss":
|
| DECIMALPARSE value |
This function converts a string (value) that contains a decimal value to decimal format. Specifying a source column for which some instances do not contain decimal values can cause the ETL job to fail. Cambridge Semantics recommends using TRYPARSEDECIMAL unless you are certain that all instances of value contain a decimal. |
| DOUBLEPARSE value |
This function converts a string (value) that contains a double value to double format. Specifying a source column for which some instances do not contain double values can cause the ETL job to fail. Cambridge Semantics recommends using TRYPARSEDOUBLE unless you are certain that all instances of value contain a double. |
| FLOATPARSE value |
This function converts a string (value) that contains float values to float format. Specifying a source column for which some instances do not contain float values can cause the ETL job to fail. Cambridge Semantics recommends using TRYPARSEFLOAT unless you are certain that all instances of value contain floats. |
| INTPARSE value |
This function converts a string (value) that contains integer values to integer format. Specifying a source column for which some instances do not contain integer values can cause the ETL job to fail. Cambridge Semantics recommends using TRYPARSEINT unless you are certain that all instances of value contain integers. |
| LONGPARSE value |
This function converts a string (value) that contains a long integer value (from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647) to long format. Specifying a source column for which some instances do not contain long values can cause the ETL job to fail. Cambridge Semantics recommends using TRYPARSELONG unless you are certain that all instances of value contain long data. |
| SHORTPARSE value |
This function converts a string (value) that contains a short integer value (from -32,678 to 32,767) to short format. Specifying a source column for which some instances do not contain short values can cause the ETL job to fail. Cambridge Semantics recommends using TRYPARSESHORT unless you are certain that all instances of value contain short data. |
| TIMEPARSE time text |
This function converts a string that contains time text to a time value in the time format that you specify. Specifying a source column for which some instances do not contain time values can cause the ETL job to fail. Use this function only when all instances of time text contain a time value.
|
| TOSTRING value |
This function converts a value that is a double data type to string format.
|
| TRYPARSEBOOLEAN value |
This function attempts to convert a string value to a boolean data type. If an instance cannot be converted, Anzo replaces the string with the value in if error.
|
| TRYPARSEDATE value |
This function attempts to convert a string value to a date data type in the date format that you specify. If an instance cannot be converted, Anzo replaces the string with the value in if error.
|
| TRYPARSEDATETIME value |
This function attempts to convert a datetime string value to a date data type in SQL date format (yyyy-MM-dd). If an instance cannot be converted, Anzo replaces the string with the value in if error.
|
| TRYPARSEDECIMAL value |
This function attempts to convert a string value to a decimal data type. If an instance cannot be converted, Anzo replaces the string with the value in if error.
|
| TRYPARSEDOUBLE value |
This function attempts to convert a string value to a double data type. If an instance cannot be converted, Anzo replaces the string with the value in if error.
|
| TRYPARSEFLOAT value |
This function attempts to convert a string value to a float data type. If an instance cannot be converted, Anzo replaces the string with the value in if error.
|
| TRYPARSELONG value |
This function attempts to convert a string value to a long data type. If an instance cannot be converted, Anzo replaces the string with the value in if error.
|
| TRYPARSESHORT value |
This function attempts to convert a string value to a short data type. If an instance cannot be converted, Anzo replaces the string with the value in if error.
|
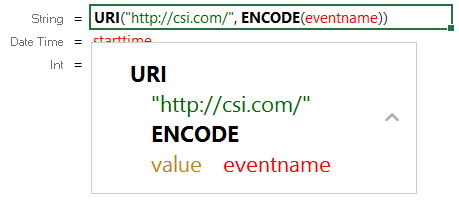
| URI() | When specified in the Source column in mappings, this function transforms the property values to URI format by concatenating each of the components that you specify in the function. To ensure that values with spaces and other characters are encoded as valid URIs, the URI function is often used with the ENCODE function. For example, the following mapping for a "tickit_events" table transforms an "eventname" string to URI format by prepending "http://csi.com/" to the encoded event names:
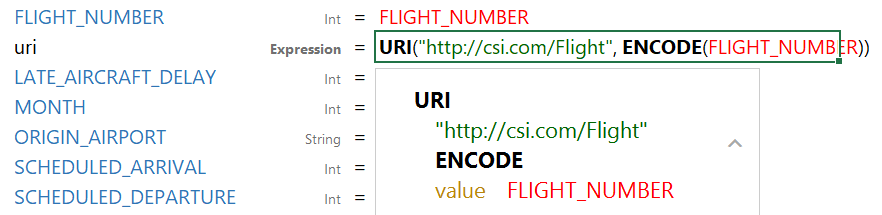
This example mapping results in triples such as: <tickit_events> <eventname> "http://csi.com/Rolling+Stones" You can also enter URI() in the Target column to specify that the Expression in the Source column should be the URI of the entity that is being created. For example, the mapping below generates an entity URI by prepending "http://csi.com/Flight" to the flight number value:
The example URI specification results in triples such as: <http://csi.com/Flight1234> <FLIGHT_NUMBER> 1234 <http://csi.com/Flight1234> <ORIGIN_AIRPORT> "BOS" |
Lookup and Mapping Functions
This section describes the lookup and map functions that Anzo supports.
| Function & Arguments | Description |
|---|---|
| LOOKUP from |
This function enables you to look up values in a supplemental table. LOOKUP joins the from lookup table to a source table on the columns specified in the fields and values arguments. The function returns the value from get in the lookup table that corresponds to each row’s value in the values argument.
|
| MAKELIST expression |
This function maps multiple source columns to a single target property. The function does not create a list; it creates new rows, one for each column that is mapped to the target.
|
| MAP value |
This function retrieves values from a map that you define. The map is a collection of key/value pairs. The function uses the specified value as a key in the map and returns the value associated with the key.
|
Numeric Functions
This section describes functions that operate on values with numeric data types.
| Function & Arguments | Description |
|---|---|
| CEILING value |
This function rounds the value up to the next whole number if the value has a fractional part.
|
| DIVIDE v1 |
This function divides the values of the numeric expressions that you specify (v1/v2).
|
| FLOOR value |
This function rounds the value down to a whole number if the value has a fractional part.
|
| MULTIPLY v1 |
This function multiplies the values of the numeric expressions that you specify (v1 x v2).
|
| NUMERIC_ADD v1 |
This function adds the values of the numeric expressions that you specify (v1 + v2).
|
| NUMERIC_SUBTRACT v1 |
This function subtracts the values of the numeric expressions that you specify (v1 - v2).
|
| RANDOM value |
This function replaces value with a random integer from within the min range and max range that you specify.
|
| ROUND value |
This function rounds the value up or down to the closest whole number.
|
String Functions
This section describes functions that operate on values with string data types.
| Function & Arguments | Description |
|---|---|
| CONCATENATE text |
This function concatenates multiple string values (text) and returns a single string.
For example, the source mapping below concatenates PATIENTHOMESTATE and PATIENTHOMEZIP:
|
| DATEPARSE date text
|
This function converts a string that contains a date value (date text) to the specified date format.
For example, the source mapping below converts the MovieReleaseDate values from strings to dates in the format "dd-MM-yyyy":
The format that you specify for dates is flexible. For example, typing the format "dd-MMM-yy" displays values such as "01-JAN-19." |
| DATETIMEPARSE date text
|
This function converts a string that contains a datetime value (date text) to the specified date format.
For example, the source mapping below converts the PATIENTLASTPMODATE from a string value to a datatime value in the format "MM-dd-yyyy HH:mm:ss":
|
|
LEFT text |
This function starts on the left side of a text string, keeps the number of characters in num chars, and returns the truncated string. |
| LOWER value |
This function converts a string value to lower case letters. |
| REGEX input |
This function finds all patterns in the input string that match the specified regular expression (regex). It replaces the input patterns with the value in replace and returns the resulting string.
For example, the source mapping below uses the REGEX function to search for the pattern "PS" in the COMPLAINTSTRING values and replaces each PS with a hyphen (-):
|
| RIGHT text |
This function starts on the right side of a text string, keeps the number of characters in num chars, and returns the truncated string. |
| SPLIT string
|
This function splits a string value into multiple values based on the specified delimiter.
|
| SPLITARRAY string
|
This function splits a string value into an array based on the delimiter. From the array, the function retrieves only the portion of the value that you specify in the index.
For example, the following source mapping retrieves only the last four digits of social security numbers:
|
| STRLEN term |
This function returns the number of characters in the specified text string (term). |
| UPPER value |
This function converts a string value to upper case letters. |