Exporting an Artifact
You can export the current version of an artifact and its related entities or any backup version. Follow the instructions below to export an artifact. For instructions on creating a backup version, see Creating a Backup Version of an Artifact.
- In the Anzo application, navigate to the artifact that you want to export.
For Data Models, add the Model that you want to export to the Working Set and then open it in the Model editor.
- Follow one of the options below, depending on whether you want to export the current version of the artifact or a backup version:
- If you want to export the current, working version of the artifact, click the Export icon (
 ) under the artifact name.
) under the artifact name.
The image below shows an example of the Export icon for an artifact that has a backup version. Clicking the Export icon (
 ) exports the current version of the artifact, not the backup version that is listed.
) exports the current version of the artifact, not the backup version that is listed.
- If you want to export a backup version of the artifact, click the Versions tab, which lists the backups that exist for the artifact. Select the Version that you want to export and then click the Export button. For example, the image below shows the Versions tab for a Graphmart:
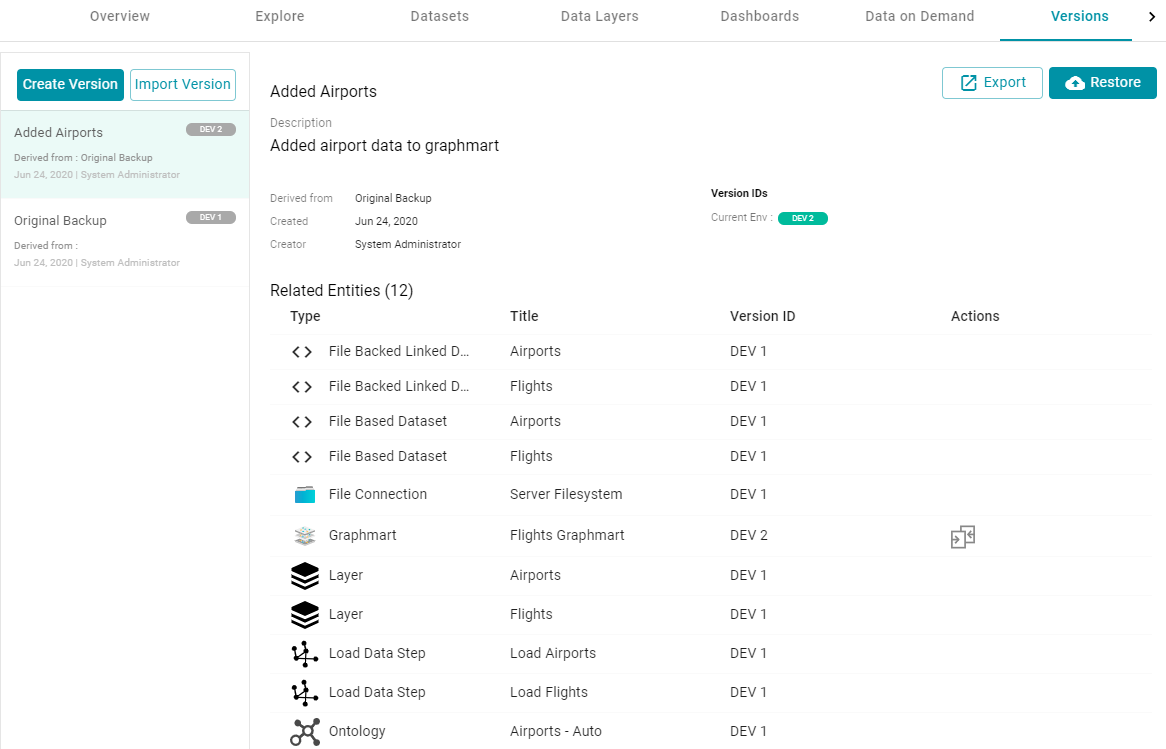
The Export dialog box is displayed. For example:
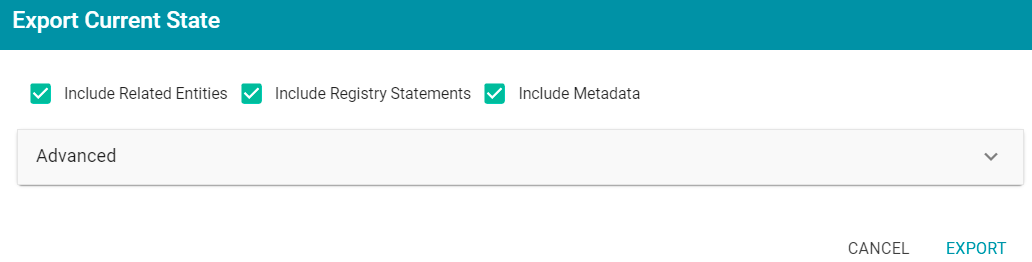
- If you want to export the current, working version of the artifact, click the Export icon (
- On the Export dialog box, configure the following export options as needed. The list below describes each option:
- Include Related Entities: Indicates whether to export the artifact's related entities. Since most artifacts have dependencies with other artifacts, Cambridge Semantics recommends that you enable Include Related Entities (selected by default) and export all related entities. The number and type of related entities that are included varies by the type of artifact that is being exported.
When exporting a pipeline, there are several artifacts that contribute to that pipeline besides the ETL jobs. Since the pipeline reads the source data, it requires the data source connection and schema artifacts. It also depends on the ontology and mapping artifacts for instructions on mapping and/or transforming the source data to the graph data model. And it requires the file store and Anzo data store artifacts to be able to write the resulting RDF data files to the appropriate location. Capturing all of the related entities ensures that the exported package includes all of the artifacts that the pipeline depends on to run successfully.
- Include Registry Statements: Indicates whether to export the registry statements for the artifact and each of its related entities.
- Include Metadata: Indicates whether to export the metadata graph for the artifact and its related entities, such as the permissions configuration and last modified date. If you exclude the metadata, the artifacts in this export will follow the metadata configuration on the destination server when they are imported. Select Include Metadata if you want to migrate the existing metadata to the destination server. Enabling this setting also gives you the option to change the permissions configuration for the exported entities.
- Include Related Entities: Indicates whether to export the artifact's related entities. Since most artifacts have dependencies with other artifacts, Cambridge Semantics recommends that you enable Include Related Entities (selected by default) and export all related entities. The number and type of related entities that are included varies by the type of artifact that is being exported.
- If you want to change permissions or replace the values for certain properties in the exported version of an entity, such as the user name and password for a Data Source, the base folder location for a file connection, or the file path for an Anzo Data Store, expand the Advanced option to view the Included Entities list. For example:
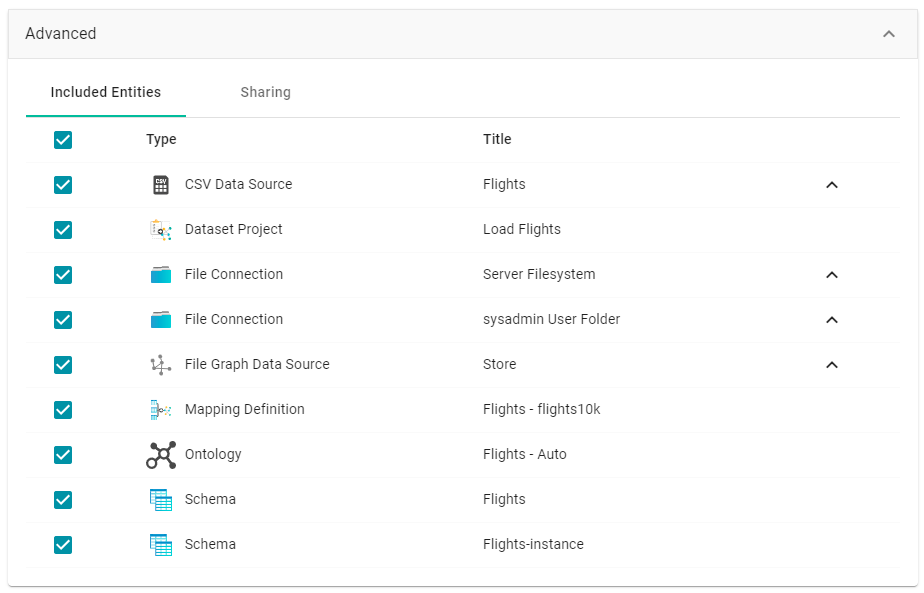
The entities with replaceable values are expandable. Click the ^ character to the right of an entity name to expand the options and view the editable properties. Replace any of the existing values with the new values that you want to define for the exported version of the artifact. For example:
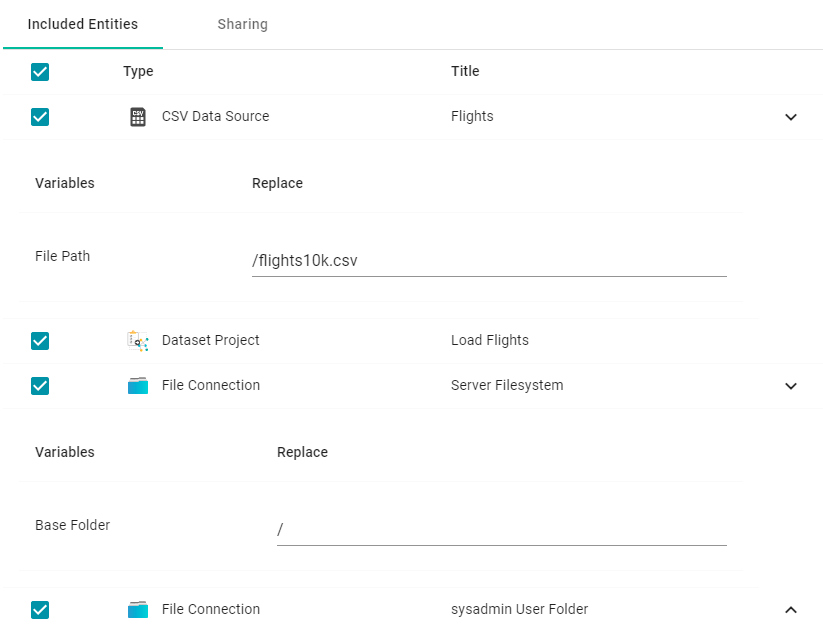
For information about configuring additional properties so that their values are replaceable on export, see Making Values Replaceable on Export.
If you specified Include Metadata and want modify permissions for the exported entities, click the Sharing tab. For information about changing permissions on the Sharing tab, see Sharing Access to Artifacts.
When a row in the Related Entities list includes the compare versions icon (
 ) in the Actions column, you can click the icon to open a side-by-side comparison of the TriG files for the two versions. For example:
) in the Actions column, you can click the icon to open a side-by-side comparison of the TriG files for the two versions. For example: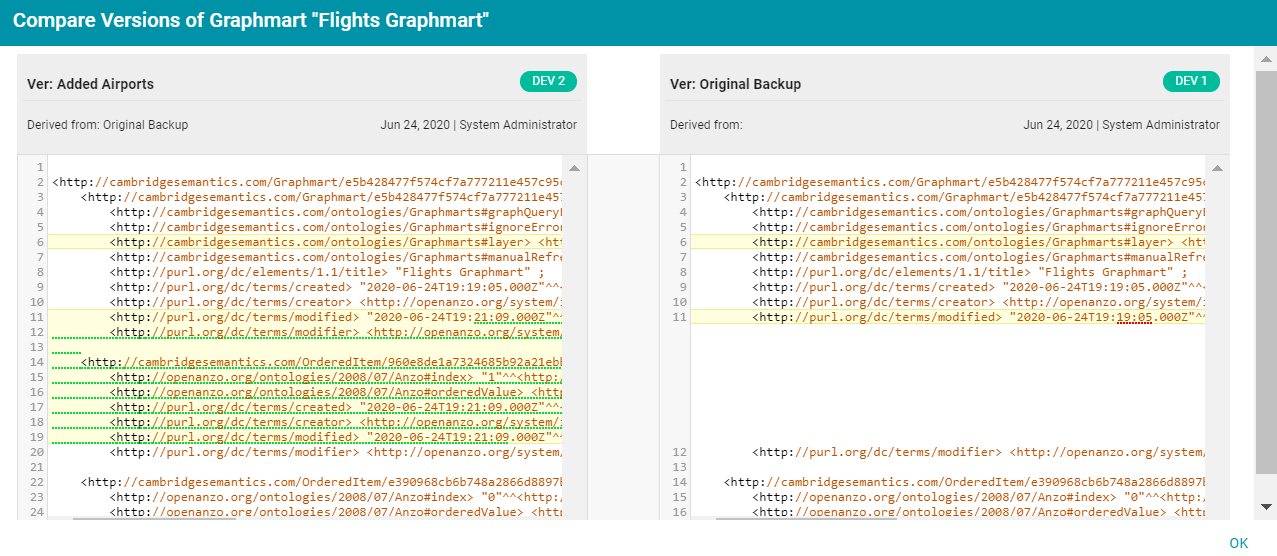
- Click Export to export the artifacts.
Anzo packages the files into a .zip file and downloads it to your computer. You do not need to extract the files in order to import the artifacts to another Anzo server. See Exported ZIP File Contents below for a description of the files that are included in the .zip file.
Exported ZIP File Contents
Depending on the options configured for the export, the resulting .zip file contains one or more of the following files:
- <artifact_name>_export.trig contains statements about the type of artifact that was exported and the export settings that were configured.
- <artifact_name>_graph.trig contains the Model, Data Source, Schema, and Mapping definitions.
- <artifact_name>_metadata.trig contains metadata statements such as the access control configuration and last modified date for the exported entities.
- <artifact_name>_registry.trig contains registry statements such as the named graph information for the Data Source, Schema, Model, and instance data.